Hip replacement is highly successful surgery in which portions of the hip joint are replaced with prostheses (implants). Most patients have a total hip replacement, but for some others, a partial replacement (hemiarthroplasty) may be appropriate.
What is hip replacement surgery?
Hip replacement is the removal and replacement of portions of the pelvis and femur (thighbone) that form your hip joint. It is performed primarily to relieve hip pain and stiffness caused by hip arthritis.
This procedure is also sometimes used to treat injuries such as a broken or improperly growing hip, and for other conditions.
How do you know if you need a hip replacement?
If you have these arthritis symptoms, you should consider a hip replacement:
- severe hip pain that is not relieved by medication and that interferes with your work, sleep or everyday activity
- hip stiffness that restricts motion and makes it difficult to walk
Healthy hip vs. arthritic hip
The hip is a ball-and-socket joint. The ball, at the top of your femur (thighbone) is called the femoral head. The socket, called the acetabulum, is a part of your pelvis. The ball moves in the socket, allowing your leg to rotate and move forward, backward and sideways.
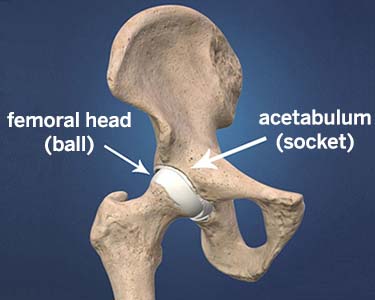
In a healthy hip, soft tissue called cartilage covers the ball and the socket to help them glide together smoothly. If this cartilage wears down or gets damaged, the bones scrape together and become rough. This condition, known as osteoarthritis, causes pain and restricts motion. An arthritic hip can make it painful for you to walk or even to get in or out of a chair. If you have been diagnosed with hip arthritis, you may not need surgery. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and/or physical therapy may provide relief. But, if these efforts do not relieve symptoms, you should consult an orthopedic surgeon.
What are the different types of hip replacement surgery?
The three major types of hip replacement are:
- total hip replacement (most common)
- partial hip replacement
- hip resurfacing
The most common type of hip replacement surgery is called a total hip replacement (also called total hip arthroplasty). In this surgery, worn-out or damaged sections of your hip are replaced with artificial implants. The socket is replaced with a durable plastic cup, which may or may not also include a titanium metal shell. Your femoral head will be removed and replaced with a ball made from ceramic or a metal alloy. The new ball is attached to a metal stem that is inserted into the top of your femur. (Learn more about types of hip implants.)
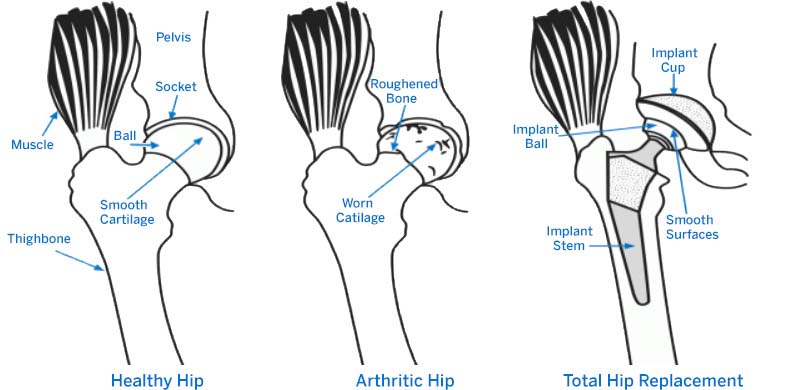
Two other types of hip replacement surgeries are each generally appropriate for patients of specific age groups and activity levels:
- Partial hip replacement (also called hemiarthroplasty) involves replacing only one side of the hip joint – the femoral head – instead of both sides as in total hip replacement. This procedure is most commonly done in older patients who have fractured their hip.
- Hip resurfacing of the femoral head and socket is most commonly done in younger, active patients.
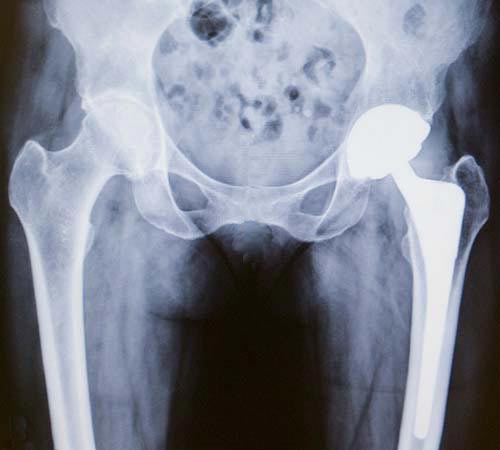
X-ray of a total hip replacement showing the ball, socket and stem implants
There are two major surgical approach methods for peforming a total hip replacement:
- the posterior approach (more common)
- the anterior approach
Posterior and anterior hip replacement surgery
The two most common surgical approaches in hip replacement are the posterior approach and anterior approach (sometimes called the “mini-anterior approach” or “muscle-sparing hip replacement”).
To begin the operation, the hip replacement surgeon will make incisions on either the back (posterior) or front (anterior) of the hip. Both approaches offer pain relief and improvement in walking and movement within weeks of surgery.
Total hip replacement animation: Posterior approach
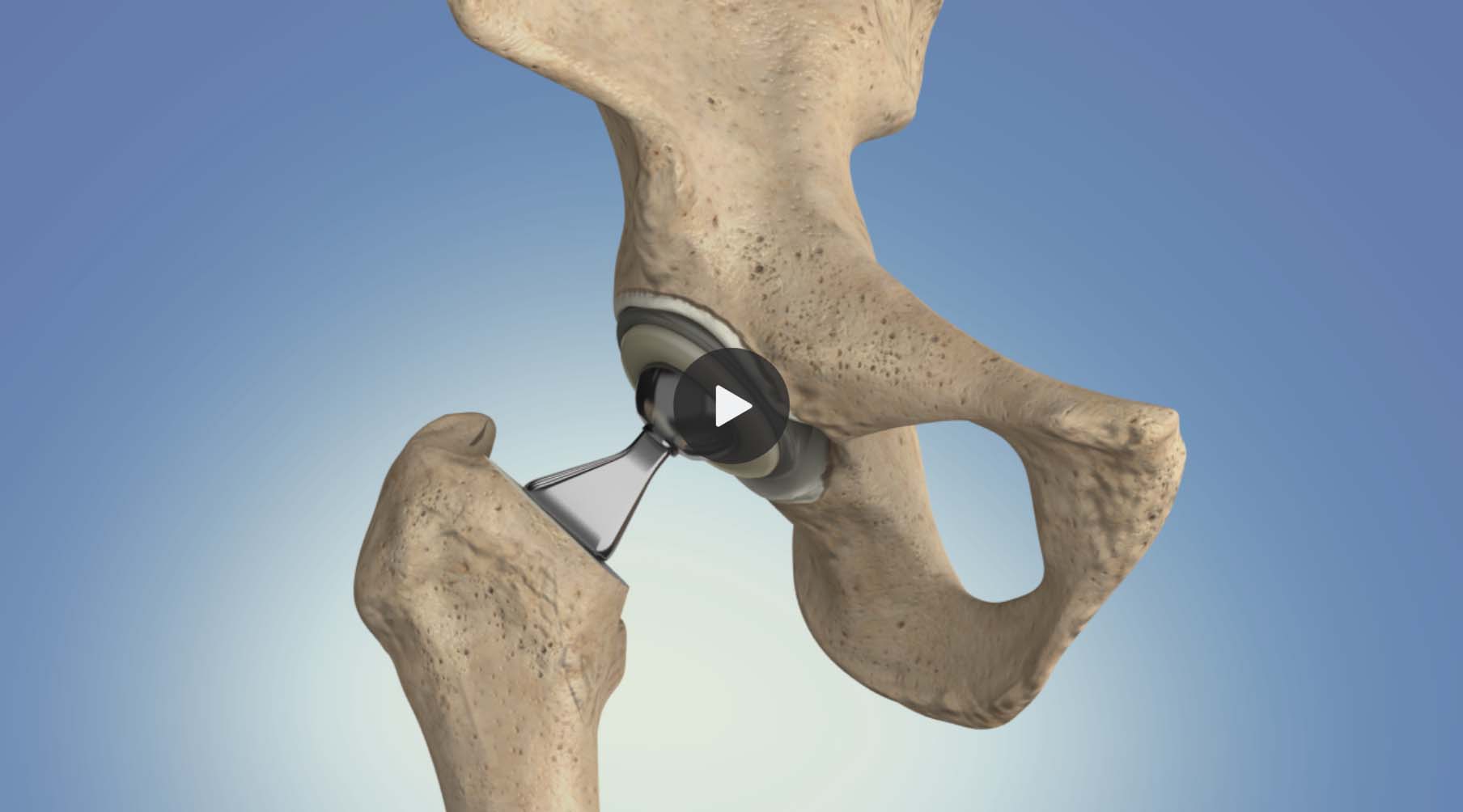
Total hip replacement animation: Anterior approach
How should I prepare for hip replacement surgery?
There are certain steps patients can take both before and after surgery to improve recovery time and results. It is important to follow the instructions and guidance provided by your orthopedic surgeon, medical team and rehabilitation therapist.
Do you stay overnight for a hip replacement?
Most patients will stay in the hospital one or two nights after surgery. Some patients may be able have same-day hip replacement and return home after an outpatient procedure.
How long does hip replacement surgery take?
Total hip replacement surgery takes about one and a half hours. Most patients also stay in the hospital for one or two days after the procedure.
What is hip replacement surgery recovery like?
Your rehabilitation will begin within 24 hours after surgery. Most hip replacement patients progress to walking with a cane, walker or crutches within day or two after surgery. As the days progress, you will increase the distance and frequency of walking.
If you have THR surgery:
- Your recovery will begin directly following surgery in the Post-Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU), where your medical team will manage your pain and monitor your vital signs.
- Once the anesthesiologist is satisfied with your condition, you will be moved to an inpatient recovery room to monitor your progress.
- You will most likely have a dressing and tube on your hip for drainage, which should be removed the day after surgery.
- The pain management team will assess your medication and use a multifaceted approach to ensure comfort and mobility during the rehabilitation process.
- You will begin rehabilitation with a physical therapist within 24 hours. Your therapist will help you sit up, get in and out of bed, and practice walking and climbing stairs using a walker, cane or sometimes crutches.
- You will then continue physical therapy outside the hospital for 6 to 8 weeks. After that period, most patients are able to do everyday activities and return to playing sports.
What are the risks of hip replacement surgery?
The surgery is very safe, but every surgery has risks, and infection is the most serious. You should ask your surgeon what the surgical infection rate is for hip replacements at the hospital or facility where you will have your surgery.
Other risks include blood clots in the leg or pelvis, and accidental hip dislocation during or after recovery. Hospital for Special Surgery performs better than the national average in preventing blood clots after surgery.
How long do hip implants last?
Generally speaking, a hip replacement prosthesis should remain effective for between 10 and 20 years, and some can last even longer.
Results vary according to the type of implant and the age of the patient. In a 2008 study of more than 50,000 patients who had THR surgery at age 55 or older, between 71% and 94% still had well-working implants after 15 years.*
(Source: Makela, Keijo T. MD; Eskelinen, Antti, et al. “Total Hip Arthroplasty for Primary Osteoarthritis in Patients Fifty-five Years of Age or Older: An Analysis of the Finnish Arthroplasty Registry.” Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery – American Volume – Vol 90 October 01, 2008.)
When a hip implant does need to be replaced because it has loosened or worn out over time, this requires what is called hip revision surgery.
Frequently asked questions about hip replacement surgery
Can I have both hips replaced at the same time?
Yes, healthy patients younger than 75 years old who have no history of cardiopulmonary disease may be able to have both hips replaced at once. In some cases, however, it may be better to stage the surgeries.
What are hip implants made of?
There are three separate implants: the stem, the ball and the socket.
- The stem, made out of metal (usually titanium or cobalt-chrome) is inserted into your natural thighbone.
- The ball is usually made out of polished metal or ceramic, and fits on top of the stem.
- The socket is usually a combination of a plastic liner and a cobalt-chrome or titanium backing.
Learn more about joint replacement prostheses by reading Understanding Implants in hip and Hip Replacement.
Will my new hip set off the metal detector at the airport?
Today’s sensitive screening machines will detect the implant but can also effectively identify it. The machine operator will know that it is an implant rather than an unauthorized metal object contained outside the body.
It is still helpful to tell airport security that you have had a hip replacement before entering the screening machine. You may also ask your doctor’s office if they can provide a card that identifies that you have received a hip implant that contains metal.
How soon after surgery can I resume driving?
Most patients can resume driving by six weeks after surgery.
What should I look for in a hip replacement surgeon?
When looking for an orthopedic surgeon to perform your hip replacement surgeon, it’s important to do your research and check the surgeon’s credentials, experience and reputation. It is also important to research the hospital or facility where you will have your operation, as well as its supporting staff, such as the anesthesiologists.
HSS has one of the lowest rates of infection for hip replacement surgery, as well as a significantly lower rate of readmission compared to the national average. HSS also performs more hip and knee replacements than any other US hospital and is ranked the No. 1 hospital for orthopedics in the United States by U.S. News and World Report. No other hospital in the world focuses solely on health problems of the bones, joints and soft tissues like muscles.
The success rate for hip replacement surgery at HSS is very high. In a study, HSS interviewed patients to learn about their progress. Two years after their surgeries, 99.4% of patients said they had relief from pain, 98.8% said their ability to move was improved, and 97.8% said their quality of life was better because of their surgery. (Source: HSS Arthroplasty Registry, 2007-2012.)
